Wheatstone Bridge
Wheatstone Bridge: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electrical Instruments, Wheatstone Bridge, Balanced Wheatstone Bridge, Unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge, and Sensitivity of Wheatstone Bridge.
Important Questions on Wheatstone Bridge
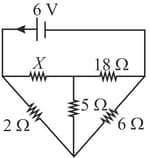
The magnitude of resistance in the circuit shown in the given figure, when no current flows through the resistor is
The voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer is given by-
Amount of deflection of the galvanometer depends on _____.
When the bridge is balanced, what is the current flowing through the galvanometer?
Figure shows an unbalanced Wheatstone bridge. What is the direction of conventional current between and ?
The figure given below shows a network of eight resistors, each equal to connected to a battery of negligible internal resistance. The current in the circuit is
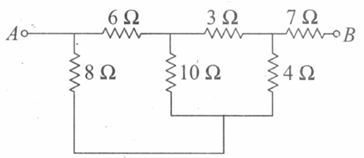
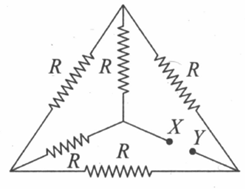
Find the equivalent resistance between and .
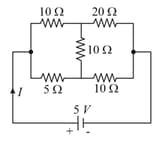
The current drawn from the source will be
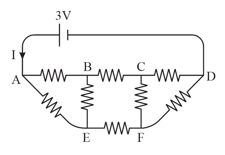
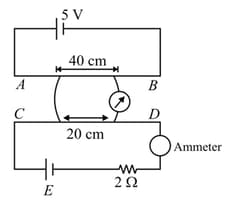
and are two uniform resistance wire of lengths and respectively. The connections are shown in the figure. The cell of emf is ideal while the other cell of emf has internal resistance A length of of wire is balanced by of wire Find emf in volt, if the reading of the ideal ammeter is The other connecting wires have negligible resistance.
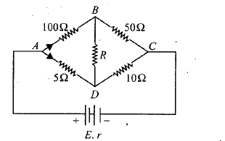
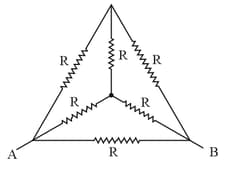
The effective resistance between and is
As shown in the figure below, a cube is formed with ten identical resistance (thick lines) and two shorting wires (dotted lines) along the arms and .
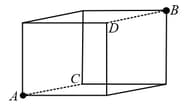
The resistance between points and is
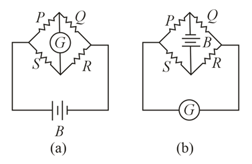
Figure below shows a Wheatstone bridge in which are fixed resistances, is a galvanometer and is a battery. For this particular case, the galvanometer shows zero deflection. Now, only the positions of and are interchanged, as shown in figure . The new deflection of the galvanometer-
Find the equivalent resistance between and .
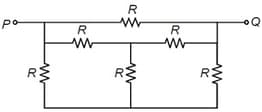
The effective resistance between points P and Q of the electrical circuit as shown in the figure is
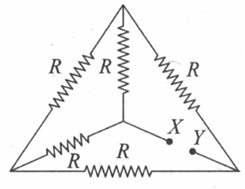
In the arrangement of resistances shown below, the effective resistance between points and is
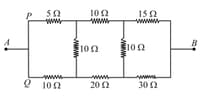
Find the equivalent resistance between the points and
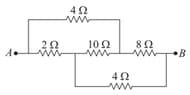
Five capacitors of capacity each are connected to a potential of volts as shown in figure. The equivalent capacitance between the points and will be equal to :-
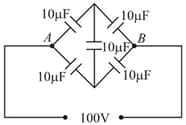
On interchanging the position of battery and galvanometer in Wheatstone bridge respectively the new balance point:
What is the equivalent resistance between the points and as in the picture below?